Chain Transfer Agents
Chain transfer agents, also called modifiers or regulators, have at least one weak chemical bond. These compounds react with the free-radical site of a growing polymer chain and interrupt chain growth. In the process of chain transfer, the radical is temporary transferred to the regulating agent which reinitiates growth by transfering the radical to another polymer or monomer:
Rr· + S → Pr + S·
S· + M → R1·
S· + Pr → Rr·
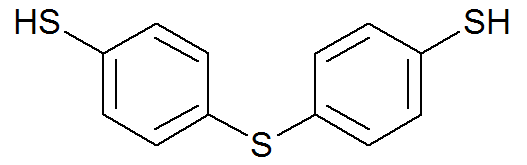
Chain-transfer agents are often added to control the chain length during synthesis to achieve certain mechanical and processing properties. Very effective chain transfer agents are halogen compounds, some aromatic hydrocarbons, and thiols (mercaptans). Some common chain transfer agents are shown below.
| Compound | Repeating Unit | Boiling Point (°C) |
| Carbon tetrachloride | CCl4 | 77 |
| Carbon tetrabromide | CBr3 | 190 |
| Bromotrichloromethane | BrCCl3 | 105 |
| 4-Methylbenzenethiol |
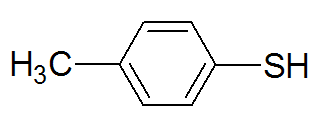 |
195 |
| Isooctyl 3-mercaptopropionate |
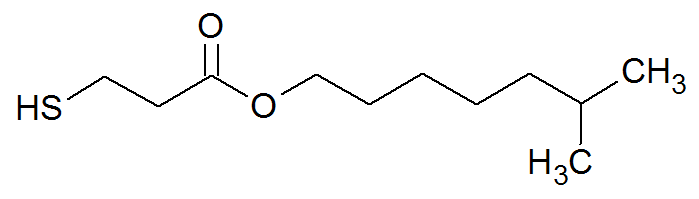 |
111 |
| Pentaphenylethane |
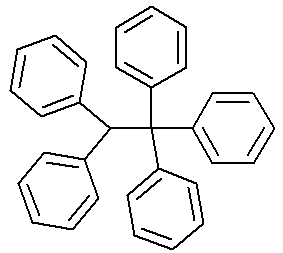 |
457 |
| tert-Nonyl mercaptan |
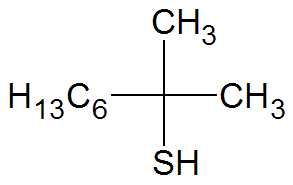 |
188 |
| 4,4′-Thiobisbenzenethiol |
 |
N/A |